

Vogt, “ Smartphones as experimental tools: Different methods to determine the gravitational acceleration in classroom physics by using everyday devices,” Eur. Thereby we measure the time between two impacts, i.e., Δ t = 2 t H. The kinetic energies E kin 1 and E kin 2 between two subsequent impacts behave like the squares of the impact velocities, and the rise and fall times t H of the ball are given with t H = v 0 g. On first bounce it comes up to a height d, corresponding to potential energy mgd.
BOUNCING BALL GRAVITY LAB FREE
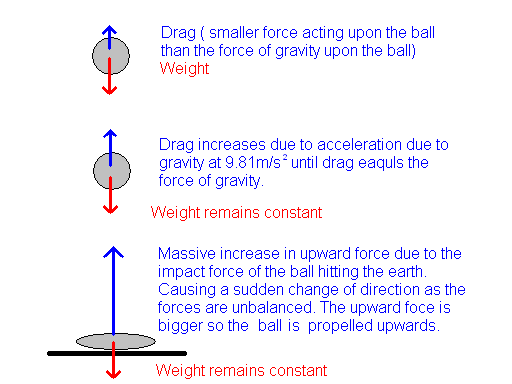
Alternatively, a commercial measuring system or a free sound editor (e.g., Audacity) can be used to make the acoustic recordings. However, if your are interested in the physics behind how balls bounce, the following principles apply: The ball begins at rest from height h with potential energy mgh, where m is its mass and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
The Oscilloscope app can be bought in the Apple Store at the following link for $19.99: /us/app/oscilloscope/id388636804. Laudares, “ Listening to the coefficient of restitution and the gravitational acceleration of a bouncing ball,” Am. This applet shows the mass bouncing from the walls of the box. You can also change the angle of the floor by dragging in the horizontal direction on the bar under the 'dip' in the floor. Once in motion, the mass can be 'caught' by clicking and holding it with the mouse.
BOUNCING BALL GRAVITY LAB TRIAL
For Trial 2, repeat steps 5 and 6 but drop the ball from a height of 50 cm. Bouncing Ball Experiment The ball starts with more GPE As there is more GPE more energy is converted into KE (The ball is going faster, KE1/2mv2, v is. The Bouncing Ball Drag the mass with the mouse to its new starting position. Drop the ball 4 more times from 40 cm, recording the bounce height each time, for a total of 5 drops.

Record the bounce height in the data table. Velasco, “ A measurement of g listening to falling balls,” Phys. For Trial 1, hold the ball at a height of 40 cm, drop the ball carefully and observe the bounce height. Vogt, “ Akustische Messungen an springenden Bällen” (translated as “Acoustic measurements of bouncing balls”), Praxis der Naturwissenschaften - Physik in der Schule (translated as Practice of Sciences - Physics in School), 3/53, 22– 25 (June 2004). We have the kinetic energy of the ball and the potential energy due to gravity. Sprockhoff, Physikalische Schulversuche, Mechanik (translated as Physical Experiments in School, Mechanics) ( Oldenbourg Verlag, Munich/Düsseldorf, 1961). This is a teaching module about bouncing balls and geometric series.
Pape, “ Fallbeschleunigung mit einem hüpfenden Ball” (translated as “Determining acceleration of free fall with Super Ball”), Praxis der Naturwissenschaften - Physik in der Schule (translated as Practice of Sciences - Physics in School), 4/49, 28– 32 (Aug. As shown in Equation 1, the ball has a gravitational potential energy that is equal to the mass of the ball, times the acceleration due to gravity, times the. */ // Extends JPanel, so as to override the paintComponent() for custom rendering codes. * One ball bouncing inside a rectangular box. Example 1: Getting Started with One Bouncing BallīouncingBallSimple.java: Writing a single ball bouncing inside a rectangular container box is straight forward, and can be accomplished with very few lines of codes, as follows: Let us begin by getting some balls bouncing, as an introduction to game programming. Record your bounce height data for each ball in the data tables below. Materials: two different types of balls, meter stick Procedure: Drop each ball from heights of 40, 80, and 120 cm. Java Game Programming Introduction - The World Of Bouncing Balls Predictions: How do you think bounce height will depend on drop height for each kind of ball Discuss both similarities and differences you expect to see.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
